Demystifying the Druid Ingestion Controller
Exploring the Functionality of the Druid Ingestion Controller in the Druid Kubernetes Operator
Introduction
Welcome to the guide to the Druid Ingestion Controller within the Druid Kubernetes Operator. In this post, we'll demystify the purpose and functionality of the ingestion controller, focusing on its role in managing ingestion specifications using a GitOps approach. We'll break down the reconcile logic and state management of the controller, making it easier for you to understand. Let's explore together!
Controller or Operator: Making Sense of Kubernetes Terminology
Understanding the terms "controller" and "operator" can sometimes lead to confusion, especially when used together. Let's clear that up. An operator can consist of multiple controllers. At their core, controllers act as state machines responsible for reconciling specific resources. While "operator" is a coined term, it essentially represents a collection of controllers. In the case of the Druid operator, we currently have two controllers (with plans for more in the future):
Druid Controller: Handles reconciliation for resources of type
Kind: Druid.Druid Ingestion Controller: Manages reconciliation for resources of type
Kind: DruidIngestion.
Why the need for a new controller ?
The Druid controller serves as a connection point between Apache Druid and the Kubernetes API. Its purpose is to synchronise the state of Druid nodes with Kubernetes objects. However, it doesn't directly communicate with the Druid API. To execute Druid-specific operations using Kubernetes manifests, we introduced a new controller dedicated to reconciling the state.
The Druid ingestion controller, on the other hand, focuses on reconciling Druid ingestion specifications. With the introduction of a new Custom Resource Definition (CRD) for Druid ingestion, this controller manages the reconciliation process for that CRD. Unlike the Druid controller, it is capable of communicating directly with the Druid API, facilitating specific tasks related to ingestion.
Druid Ingestion Controller
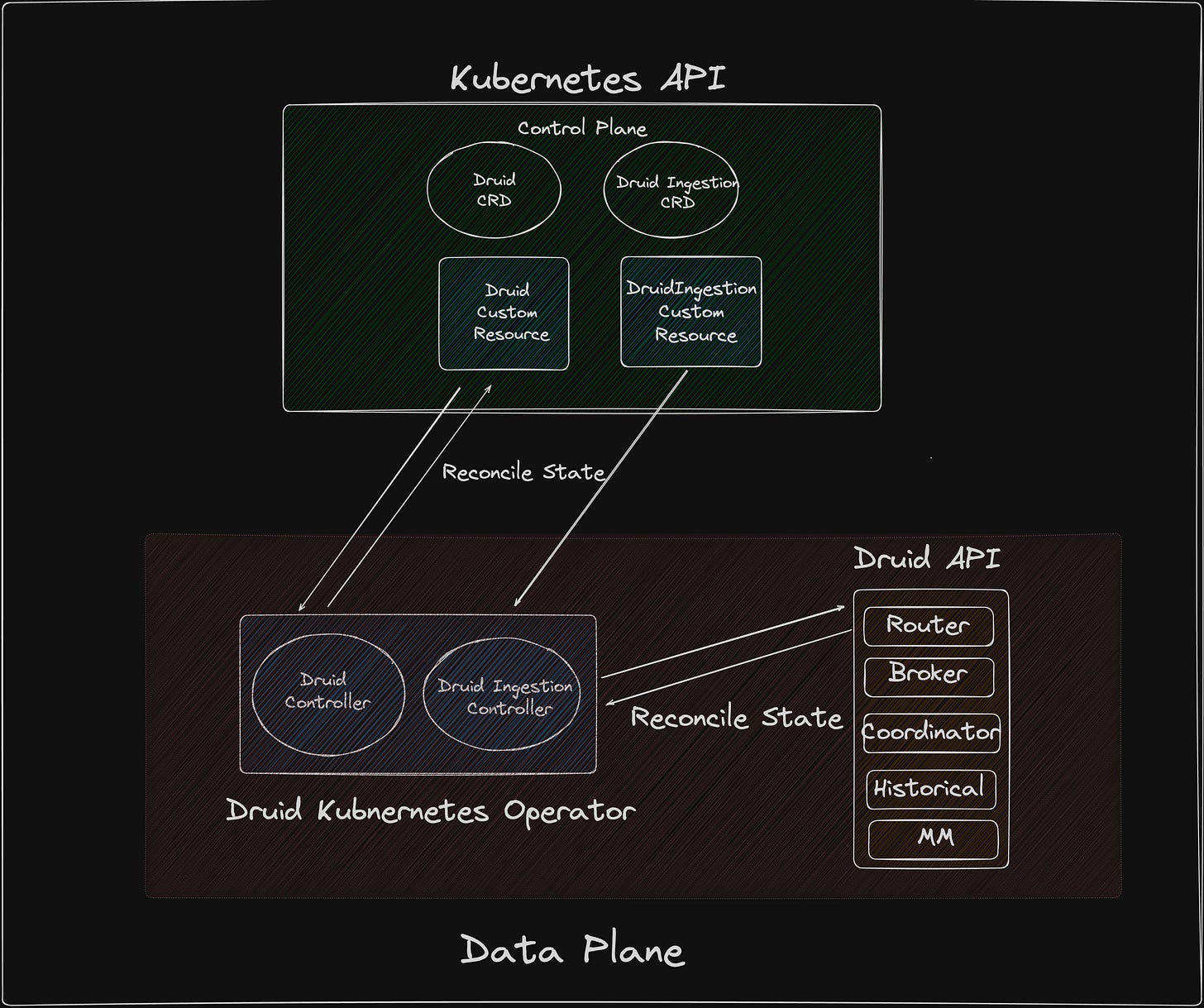
The Druid Ingestion Controller operates within the following scheme:
Group: druid.apache.org
Version: v1alpha1
Kind: DruidIngestionThe controller manages the synchronisation of custom resources for Druid ingestion. Below is a simplified diagram illustrating the main components:
With the addition of the DruidIngestion Custom Resource Definition (CRD), users can define and manage ingestion configurations more efficiently. This CRD is scoped to the Kubernetes namespace, ensuring proper isolation and organization of resources. Installation options include Helm and kubectl, providing flexibility for users to deploy the operator according to their preferences.
While currently supporting NativeBatchIndexParallel. Future updates are planned to extend support for other ingestion methods and authentication mechanisms, such as Kafka, Kinesis and QueryControllerSQL.
Please note that, the druid ingestion controller reads from the Kubernetes API and writes directly the druid API where as druid controller reads from the Kubernetes API and write to the Kubernetes API.
State Management
The Ingestion Controller, based on event-driven and polling mechanisms, ensures seamless reconciliation of Kubernetes events with druidingestion custom resources, maintaining backward compatibility with the existing Druid CR.
The internals of the Druid Ingestion Controller are designed for efficient management and synchronization of Druid ingestion processes within Kubernetes environments. Key aspects of its functionality include:
Statelessness and Status Handling: Controllers operate in a stateless manner, relying on the custom resource status to store and reflect state changes. Each reconcile loop constructs the state based on observation.
Flow for Creation and Updation of DruidIngestion CR:
The controller checks the status of the CR to determine if a taskId is associated with the incoming event.
If no taskId is associated, the controller creates a task by invoking the underlying Druid API for the specified ingestion method.
Upon submission of the request to the Druid API, the controller patches the response onto the Druid ingestion CR. A successful response (status code 200) populates the taskId, ensuring awareness of task existence in subsequent reconciliations. In case of a non-200 response, the status is updated with "failed" and the corresponding error message from the Druid API.
If a taskId is already associated with the event, the controller compares the current ingestion spec with the previous one. Any changes trigger updates to the spec via calls to the Druid API, with responses patched to the status.
Flow for Deletion of DruidIngestion CR:
The DruidIngestion controller utilises finalisers to execute logic before CR deletion.
Finalisers are added to the Druid ingestion CR if the deletion timestamp is unset.
Upon deletion of the CR, the controller sets the deletion timestamp and calls the Druid API to terminate the associated task.
Successful responses lead to finalizer removal, allowing Kubernetes API to delete the underlying CR.
Druid Service Construction and Authentication:
The controller constructs the Druid service by obtaining the router Kubernetes service, expecting the presence of the
druidClustername in the CR.Basic Auth is supported, enabling users to create a secret and reference it in the DruidIngestion CR, with controllers retrieving
OperatorUserNameandOperatorPassword.
These internal mechanisms ensure seamless orchestration of Druid ingestion processes, providing management capabilities within Kubernetes environments.
Getting Started
Here’s an example of druid ingestion CR. Prior to creating CR, lets first create a druid ingestion CRD. Note: We are assuming you already have a druid cluster up and running.
CRD
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datainfrahq/druid-operator/master/config/crd/bases/druid.apache.org_druidingestions.yamlDruid Ingestion CR
Druid CR has a few fields which you might want to tweak according to your environment.
spec:
suspend: false
druidCluster: <change_to_your_druid_cr_name>If you want to know what is the name of your druid CR. You can run this command.
kubectl get druid -n <namespace>Make sure you deploy the ingestion CR in the same namespace as your druid CR.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datainfrahq/druid-operator/master/examples/ingestion.yaml -n <namespace>Check out your druid UI, you should see an ingestion task up and running !!
Thank you for taking the time to read this post. If you have any questions, encounter bugs, or have suggestions for improvements, please don't hesitate to open an issue on the repository. Additionally, feel free to reach out to me via LinkedIn for further discussion. Your feedback is valuable and greatly appreciated.